
Emerging technologies have driven the performance boundaries of the centrifugal versus centripetal force, offering improved acceleration rates and greater throughput of samples. Programmable features and touchscreens give users more control over every operation stage. Temperature-controlled centrifugal versus centripetal force in delicate biological processes guarantee specimen stability over extended cycles. Maintenance-friendly designs and auto-diagnostic programs minimize downtime. The adaptability of next-generation centrifugal versus centripetal force devices ensures compatibility with any sample type, ranging from microfluidic volumes to industrial suspensions, making it a vital tool in scientific and engineering studies.

centrifugal versus centripetal force technology is a principal component in diverse manufacturing processes. In wastewater treatment, centrifugal versus centripetal force assist in separating sludge from liquids to improve recycling efficiency. In the manufacture of cosmetics, centrifugal versus centripetal force facilitate even emulsion and cream mixing. Crop research facilities apply it to analyze soil nutrients and plant extracts. It is also used in the manufacture of vaccines through the purification of viral particles and protein fractions. Through the ability to adapt to many substances and work requirements, centrifugal versus centripetal force continues to support industries seeking consistency, purity, and scalability.
centrifugal versus centripetal force will integrate digital intelligence and cutting-edge engineering in the years to come. Complex algorithms will auto-tune parameters for optimum efficiency and safety. Energy-optimized designs will keep operating costs at a minimum and help support global green efforts. Robotics integration will facilitate round-the-clock unattended operation in big production setups. Modular design will provide ease of customization, allowing users to set up centrifugal versus centripetal force for specific scientific or industrial uses. These improvements will allow centrifugal versus centripetal force to not only increase performance but also establish new standards for automation, accuracy, and sustainability in the lab environments of the future.

Maintenance procedure routines protect the performance and safety of centrifugal versus centripetal force. The rotor needs to be visually inspected before each operation for cracks or corrosion. Mild detergents are needed for cleaning, followed by thorough drying to prevent rust. Calibration verification and vibration monitoring assist in keeping it accurate. The instrument should be set on a level surface to reduce stress on bearings. During storage, centrifugal versus centripetal force must be kept covered and not plugged to keep electronics safe. Under operator discipline and regular maintenance, laboratories can offer years of trouble-free performance.
A centrifugal versus centripetal force makes the principle of rotational motion a tool of scientific inquiry and industrial productivity. Unrelenting spinning power applied to it fractions different materials in a sample on the basis of weight. It makes necessary procedures such as the analysis of blood, protein separation, and sewage treatment possible. centrifugal versus centripetal force today combine strength with precision by offering variable speed ranges and advanced control mechanisms. Their use also extends beyond laboratories to fields like aerospace and environmental monitoring, showing both their scientific and utilitarian applications.
Q: What factors affect the performance of a centrifuge? A: Performance depends on rotor design, speed accuracy, load balance, and regular maintenance of mechanical and electrical parts. Q: How should a centrifuge be cleaned? A: Use a soft cloth and mild detergent to clean the chamber and rotor, avoiding abrasive or corrosive substances that could cause damage. Q: Can a centrifuge be used for temperature-sensitive samples? A: Yes, refrigerated models are designed to maintain stable temperatures, protecting samples from heat generated during rotation. Q: What does RPM mean in centrifuge operation? A: RPM stands for revolutions per minute, indicating how fast the rotor spins—higher RPMs generate stronger centrifugal forces. Q: When should the rotor of a centrifuge be replaced? A: Rotors should be replaced when signs of fatigue, corrosion, or cracking appear, or after reaching the manufacturer’s specified lifespan.
The hospital bed is well-designed and very practical. Patients find it comfortable, and nurses appreciate how simple it is to operate.
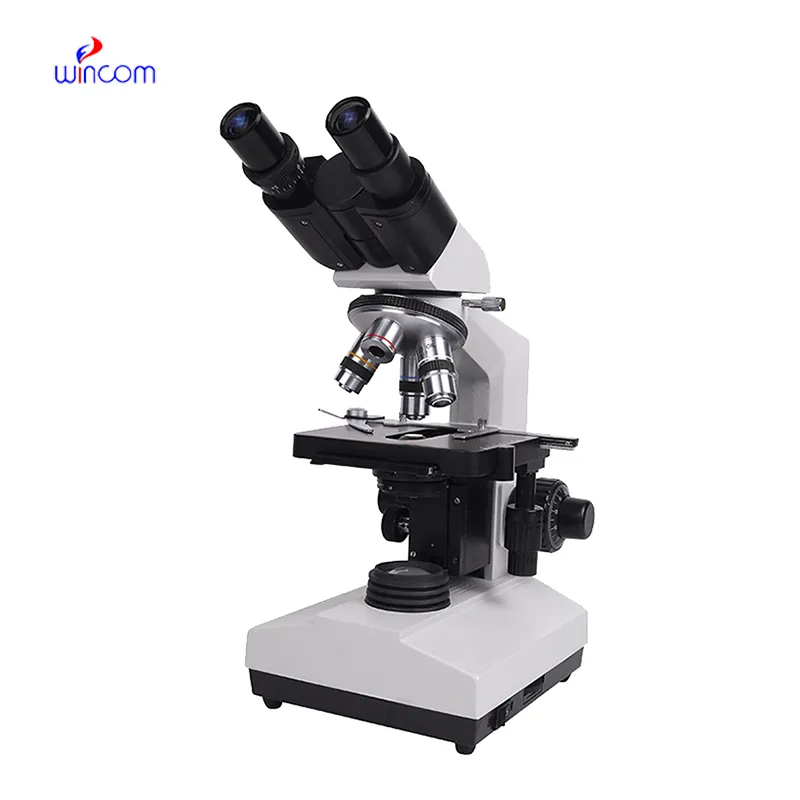
The microscope delivers incredibly sharp images and precise focusing. It’s perfect for both professional lab work and educational use.
To protect the privacy of our buyers, only public service email domains like Gmail, Yahoo, and MSN will be displayed. Additionally, only a limited portion of the inquiry content will be shown.
Hello, I’m interested in your centrifuge models for laboratory use. Could you please send me more ...
Hello, I’m interested in your water bath for laboratory applications. Can you confirm the temperat...
E-mail: [email protected]
Tel: +86-731-84176622
+86-731-84136655
Address: Rm.1507,Xinsancheng Plaza. No.58, Renmin Road(E),Changsha,Hunan,China